You’ve probably seen posts saying “eat more protein” or “protein is important for your body” and thought, “Okay… but what does protein actually do?” Whether you’re scrolling TikTok fitness videos, reading a diet blog, or just trying to eat healthier, understanding protein is key.
Protein isn’t just for bodybuilders—it’s a nutrient your body relies on for nearly every function, from repairing muscles to supporting immunity.
Quick Answer:
Protein is an essential macronutrient made of amino acids. It builds, repairs, and maintains tissues, supports metabolism, hormones, and enzymes, and keeps your body running efficiently.
🧠 What Does Protein Do for Your Body?
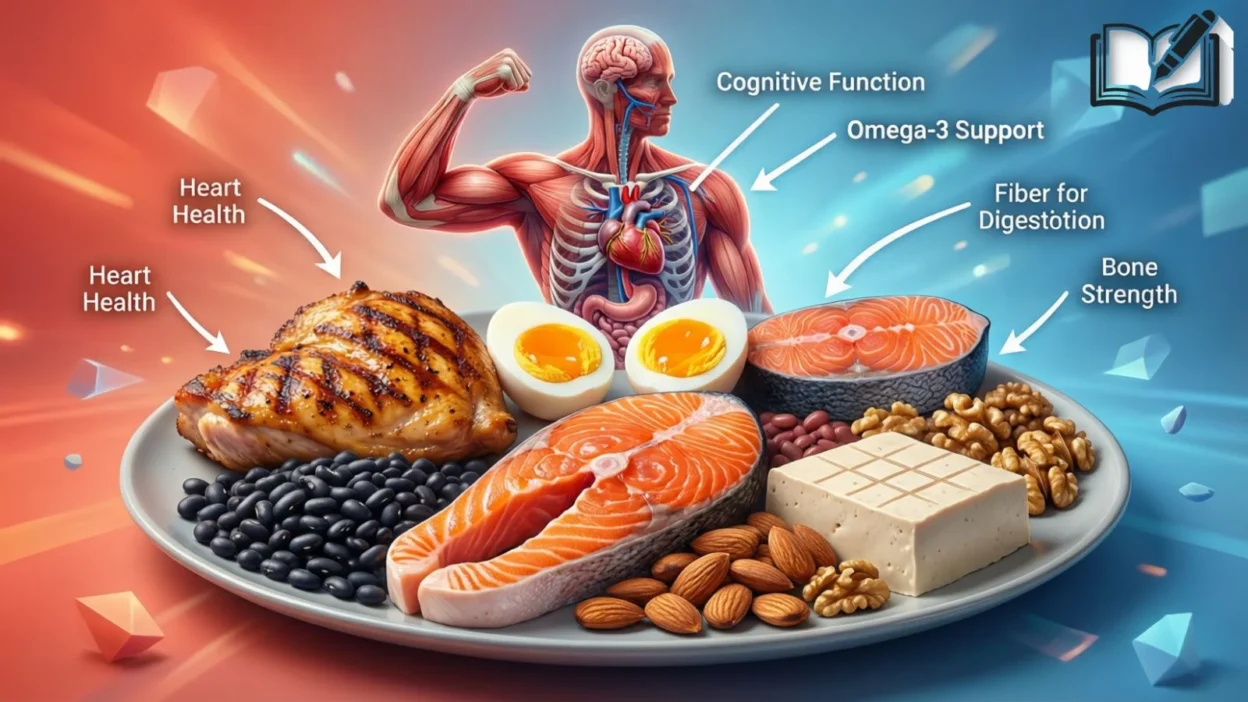
Protein is critical for growth, repair, and overall body function. Your body breaks protein down into amino acids, which are the building blocks for:
- Muscles and tendons
- Hair, skin, and nails
- Hormones like insulin
- Enzymes for digestion and metabolism
- Antibodies that support your immune system
Example:
After a workout, protein helps repair small muscle tears, promoting muscle growth and strength.
In short:
Protein = essential nutrient = supports muscles, immunity, metabolism, hormones, and overall health
🔬 9 Key Functions of Protein in the Body
- Muscle Growth & Repair 💪
Protein repairs micro-tears from exercise and builds new muscle fibers. - Immune System Support 🛡️
Antibodies are made of protein, helping fight infections. - Enzyme Production ⚙️
Enzymes control digestion, metabolism, and other chemical reactions. - Hormone Regulation 🧠
Protein helps produce insulin, glucagon, and other hormones that regulate energy and mood. - Transport & Storage 🚚
Hemoglobin (a protein) carries oxygen, and ferritin stores iron. - Structural Support 🏗️
Collagen and keratin strengthen skin, bones, and hair. - Fluid & pH Balance ⚖️
Proteins help regulate blood volume and acidity, keeping organs healthy. - Energy Source 🔥
When carbs are low, protein can provide fuel for energy. - Satiety & Weight Management 🍽️
Protein keeps you full longer, helping control appetite and reduce overeating.
📊 How Much Protein Do You Need?
| Group | Daily Protein Recommendation | Notes |
| Sedentary Adults | 0.8 g/kg body weight | Minimum requirement |
| Active Adults | 1.2–1.7 g/kg | Supports exercise recovery |
| Athletes | 1.6–2 g/kg | Muscle growth and repair |
| Seniors | 1–1.2 g/kg | Prevents muscle loss |
| Weight Loss | 1.5–2 g/kg | Supports satiety and fat loss |
Tip: Spread protein intake across meals for optimal absorption.
📱 Where Protein Is Commonly Discussed
Protein is everywhere in health and wellness contexts:
- 🏋️ Fitness blogs & gym guides
- 🥗 Diet & nutrition plans
- 📸 TikTok & Instagram health content
- 💬 Q&A forums about weight loss or nutrition
- 📚 Health or biology classes
Usage style: Informational, educational, and health-focused. Not casual slang.
💬 Real-Life Protein Conversations
A: i’m trying to eat healthier
B: add protein 😅 keeps you full and builds muscles
A: will protein help me lose weight?
B: yes, it boosts metabolism and reduces cravings
A: should i get protein from plants or meat?
B: both! plant protein works too, just mix sources
A: does protein only help gym people?
B: nope, everyone needs it for immunity and repair
A: i want stronger hair & nails
B: eat enough protein, it helps hair, skin, and nails grow
🕓 When to Focus on Protein (and When Not To)
✅ When to Use
- Muscle building and recovery
- Weight management and appetite control
- Supporting immunity and hormones
- General health and energy maintenance
❌ When Not to Focus
- Over-relying on protein supplements without real food
- Ignoring carbs and fats completely
- Medical conditions requiring restricted protein intake
Context Comparison Table
| Context | Example Phrase | Why It Works |
| Friend Chat | “protein keeps me full 😄” | Casual & relatable |
| Gym Talk | “protein helps muscle recovery 💪” | Educational & accurate |
| Work Chat | “balanced nutrition improves energy” | Professional & clear |
| Health Article | “protein function in the human body is essential” | Formal & credible |
🔄 Types and Sources of Protein
| Type | Example Foods | Notes |
| Complete Protein | Eggs, meat, fish, dairy | Contains all essential amino acids |
| Incomplete Protein | Beans, lentils, nuts | Combine to get all amino acids |
| Plant Protein | Tofu, soy, quinoa | Ideal for vegetarians & vegans |
| Animal Protein | Chicken, fish, eggs | High bioavailability |
❓ FAQs About Protein
1. Can protein help with weight loss?
Yes. Protein increases satiety, preserves muscle, and boosts metabolism.
2. Is too much protein bad?
Excess protein may strain kidneys in people with kidney disease. For healthy adults, it’s generally safe.
3. How does plant protein compare to animal protein?
Plant protein can meet needs if you eat a variety of sources to get all essential amino acids.
4. When should I eat protein for best results?
Spread across meals, with a focus on post-workout intake for muscle repair.
5. What happens if I don’t eat enough protein?
Muscle loss, fatigue, weak immunity, slow healing, and hair or skin issues.
🧠 Final Takeaway
Protein is much more than a “muscle food.” It repairs tissues, builds muscle, supports immunity, regulates hormones, and keeps you full and energized. Everyone needs it, whether you’re active or not.
Eating balanced amounts from varied sources ensures your body functions optimally. Now you know exactly what protein does for your body—and why it’s essential every single day 💪✨